Keyboard Behavior and Focus
Introduction
When you're using text fields in your app, you want to make sure the keyboard works smoothly and users can easily move between different fields. Think of it like having a smart helper that knows when to show the keyboard, what type of keyboard to show, and how to help users move between fields. Let's learn how to make your app's keyboard behavior user-friendly!
Quick Reference: Keyboard Features
| Feature | What It Does | When to Use It |
|---|---|---|
| KeyboardOptions | Controls keyboard type and actions | When you need specific keyboard types |
| ImeAction | Sets keyboard action button behavior | For navigation between fields |
| FocusRequester | Manages focus between fields | For multi-field forms |
| KeyboardActions | Handles keyboard button presses | For custom keyboard behavior |
Basic Keyboard Concepts
When to Use Keyboard Options
- When collecting different types of input (text, numbers, email)
- For forms with multiple fields
- When you need specific keyboard layouts
- For better user experience in data entry
- When you want to control keyboard behavior
Common Keyboard Types
| Keyboard Type | What It Shows | When to Use It |
|---|---|---|
| Text | Regular keyboard (letters and numbers) | For general text input |
| Email keyboard with @ symbol | For email addresses | |
| Password | Password keyboard (hides characters) | For password fields |
| Number | Number keyboard | For numeric input |
| Phone | Phone number keyboard | For phone numbers |
| Url | URL keyboard with .com button | For web addresses |
Common IME Actions
| Action | What It Does | When to Use It |
|---|---|---|
| Next | Moves focus to next field | For multi-field forms |
| Done | Hides keyboard | For final field in form |
| Go | Triggers "Go" action | For navigation actions |
| Search | Triggers search | For search fields |
| Send | Triggers send action | For message sending |
Basic Keyboard Options Example
Let's start with a simple example that shows how to set up different keyboard options:
@Composable
fun TextInputExample() {
var text by remember { mutableStateOf("") }
OutlinedTextField(
value = text,
onValueChange = { text = it },
label = { Text("Enter your name") },
// Set keyboard options
keyboardOptions = KeyboardOptions(
// Set keyboard type to text
keyboardType = KeyboardType.Text,
// Set IME action to "Done"
imeAction = ImeAction.Done
),
// Handle the "Done" action
keyboardActions = KeyboardActions(
onDone = {
// Hide the keyboard when "Done" is pressed
LocalFocusManager.current.clearFocus()
}
)
)
}
What This Example Is Doing
TextInputExample keeps text in state and shows one OutlinedTextField with label "Enter your name." keyboardOptions sets keyboardType = KeyboardType.Text (letters and numbers) and imeAction = ImeAction.Done so the keyboard shows a "Done" key. keyboardActions = KeyboardActions(onDone = { ... }) runs when the user taps Done; inside it, LocalFocusManager.current.clearFocus() clears focus and hides the keyboard. So the user gets a text keyboard, a Done button, and the keyboard dismisses when Done is pressed.
Phone Keyboard Example
For phone number fields, use KeyboardType.Phone so the device shows a numeric keypad suited for dialing (digits, +, and symbols like * and #). This makes it faster for users to enter numbers and avoids showing the full text keyboard.
@Composable
fun PhoneInputExample() {
var phone by remember { mutableStateOf("") }
OutlinedTextField(
value = phone,
onValueChange = { phone = it },
label = { Text("Phone number") },
keyboardOptions = KeyboardOptions(
keyboardType = KeyboardType.Phone,
imeAction = ImeAction.Done
),
keyboardActions = KeyboardActions(
onDone = { LocalFocusManager.current.clearFocus() }
),
singleLine = true
)
}
What This Example Is Doing
PhoneInputExample keeps phone in state and shows one OutlinedTextField with label "Phone number." keyboardOptions sets keyboardType = KeyboardType.Phone, so when the user taps the field, the system shows the phone-style keyboard (numeric keypad) instead of the full text keyboard. imeAction = ImeAction.Done and keyboardActions(onDone = { ... }) hide the keyboard when the user presses Done. Use KeyboardType.Phone whenever you are collecting a phone number so users get the right keyboard without switching.
Advanced Focus Management
Moving Between Fields
When you have multiple text fields, you want users to be able to easily move between them. This is where FocusRequester comes in handy. It's like having a helper that knows which field should get the keyboard focus next!
@Composable
fun FocusExample() {
// Create focus requesters for each field
val nameFocus = remember { FocusRequester() }
val emailFocus = remember { FocusRequester() }
val passwordFocus = remember { FocusRequester() }
Column {
// Name field
OutlinedTextField(
value = name,
onValueChange = { name = it },
label = { Text("Name") },
// Set focus requester
focusRequester = nameFocus,
// Move to email field when "Next" is pressed
keyboardOptions = KeyboardOptions(
imeAction = ImeAction.Next
),
keyboardActions = KeyboardActions(
onNext = {
emailFocus.requestFocus()
}
)
)
// Email field
OutlinedTextField(
value = email,
onValueChange = { email = it },
label = { Text("Email") },
focusRequester = emailFocus,
keyboardOptions = KeyboardOptions(
keyboardType = KeyboardType.Email,
imeAction = ImeAction.Next
),
keyboardActions = KeyboardActions(
onNext = {
passwordFocus.requestFocus()
}
)
)
// Password field
OutlinedTextField(
value = password,
onValueChange = { password = it },
label = { Text("Password") },
focusRequester = passwordFocus,
keyboardOptions = KeyboardOptions(
keyboardType = KeyboardType.Password,
imeAction = ImeAction.Done
),
keyboardActions = KeyboardActions(
onDone = {
// Hide keyboard when done
LocalFocusManager.current.clearFocus()
}
)
)
}
}
What This Example Is Doing
FocusExample uses a FocusRequester for each of the three fields (name, email, password). Each field has focusRequester = ... so the parent can move focus. The name field uses ImeAction.Next and keyboardActions(onNext = { emailFocus.requestFocus() }), so pressing Next on the keyboard moves focus to the email field. The email field does the same to move to the password field and uses KeyboardType.Email. The password field uses ImeAction.Done and onDone = { LocalFocusManager.current.clearFocus() } to hide the keyboard. So the user can move name → email → password with the keyboard and then dismiss it. (In the full app, name, email, and password would be state variables declared in the composable.)
This example shows how to:
- Create focus requesters for each field
- Move focus automatically when the user presses "Tab" or the "Next" button if there is one (might be an arrow key)
- Show different keyboard types for different fields. There are six different keyboard types:
- Text: Regular keyboard (letters and numbers)
- Email: Email keyboard with @ symbol
- Password: Password keyboard (hides characters)
- Number: Number keyboard
- Phone: Phone number keyboard
- Url: URL keyboard with .com button
- Hide the keyboard when the user is done
How these examples render
The images below show the keyboard and focus behavior. The snippets above are only part of the code; to see and run the full project, go to my GitHub page and open the chapter7 keyboard.kt file.
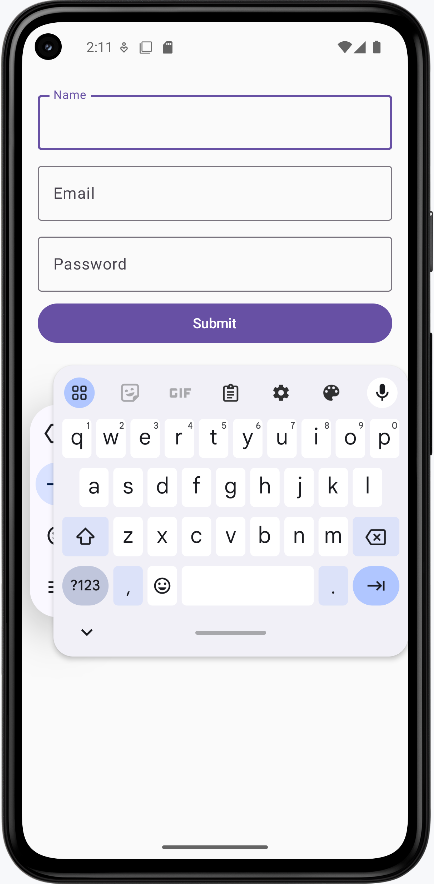
- First image: The name field is focused and the text keyboard is showing.
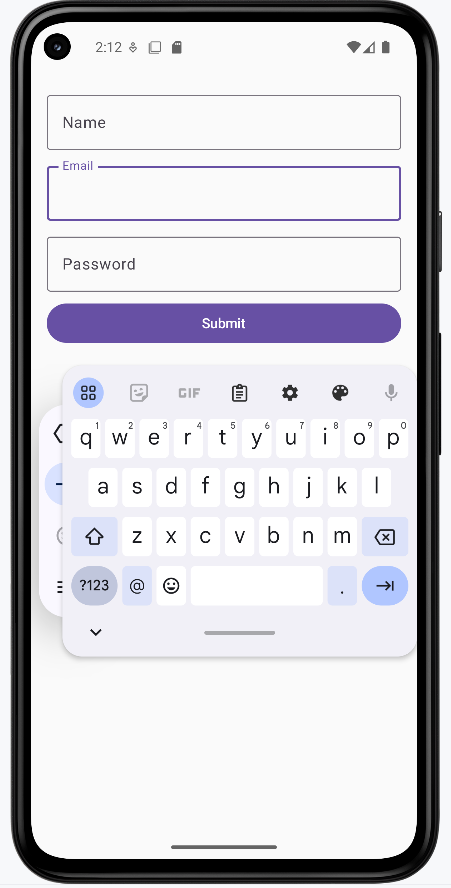
- Second image: Focus has moved to the email field and the keyboard has switched to the email keyboard (e.g. with @).
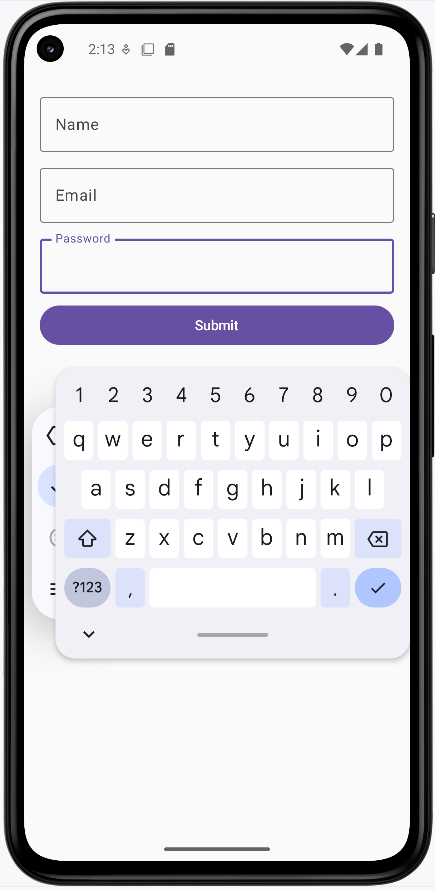
- Third image: The password field is focused and the keyboard has switched to the password type (e.g. character hiding).
Focus Management Tips
- Use FocusRequester for each field that needs focus
- Set appropriate ImeAction for each field
- Handle focus changes in keyboardActions
- Clear focus when form is complete
- Consider the natural flow of data entry
Tips for Success
- Choose the right keyboard type for each field
- Make focus movement intuitive and natural
- Clear focus when users are done
- Keep keyboard behavior consistent
- Ensure fields are visible when keyboard is shown
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using wrong keyboard type for input
- Not handling focus properly
- Leaving keyboard visible when not needed
- Inconsistent keyboard behavior
- Not considering screen space with keyboard
Best Practices
- Use appropriate keyboard types
- Implement smooth focus navigation
- Handle keyboard actions properly
- Consider user experience
- Test on different screen sizes