Bottom Sheets and Dialogs
What are Bottom Sheets and Dialogs?
Think of bottom sheets and dialogs like pop-up menus in a restaurant. When you want to see the dessert menu, the waiter brings it to your table (that's like a dialog). When you want to see the daily specials, they might slide a card across the table (that's like a bottom sheet). These UI elements help you show additional information without taking over the entire screen.
Bottom sheets slide up from the bottom of the screen, while dialogs appear in the center and dim the background. Both are great ways to show extra options, confirm actions, or display additional content without losing context of what's behind them.
Quick Reference
| Component | Description | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| Bottom Sheet | Slides up from bottom of screen | Showing options, filters, or additional content |
| Dialog | Appears in center with dimmed background | Confirming actions, showing alerts, or important messages |
When to Use Bottom Sheets and Dialogs
Use Bottom Sheets When:
- You want to show multiple options or filters
- You need to display additional content without losing context
- You want to provide a quick way to access related features
- You're showing a list of items that users can select from
- You want to save space on the main screen
Use Dialogs When:
- You need to confirm an important action (like deleting something)
- You want to show an error message or alert
- You need to get user input for a specific task
- You want to display critical information that requires attention
- You're asking for permission or showing terms of service
Practical Example
Simple Alert Dialog adn Options Bottom Sheet
class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
// Configure the status bar to use dark icons for better visibility
// This ensures the status bar icons are visible against light backgrounds
WindowCompat.getInsetsController(window, window.decorView).isAppearanceLightStatusBars = true
// Set up the Compose UI with MaterialTheme
setContent {
MaterialTheme {
MyScreen()
}
}
}
}
@Composable
fun MyScreen() {
// State variables to control the visibility of overlays
var showDeleteDialog by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
var showOptionsSheet by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
// Main content column with buttons
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.padding(16.dp)
.padding(top = 50.dp) // Extra top padding to avoid status bar
) {
// Button to show the options bottom sheet
Button(onClick = { showOptionsSheet = true }) {
Text("Show Options")
}
// Button to show the delete confirmation dialog directly
Button(onClick = { showDeleteDialog = true }) {
Text("Delete Item")
}
}
// Conditional rendering of the options bottom sheet
// This demonstrates how to show a modal bottom sheet
if (showOptionsSheet) {
OptionsBottomSheet(
onDismiss = { showOptionsSheet = false },
onOptionSelected = { option ->
// Handle the selected option from the bottom sheet
when (option) {
"Delete" -> showDeleteDialog = true // Chain to dialog
"Edit" -> { /* Handle edit action */ }
"Share" -> { /* Handle share action */ }
}
}
)
}
// Conditional rendering of the delete confirmation dialog
// This demonstrates how to show an alert dialog
if (showDeleteDialog) {
DeleteConfirmationDialog(
onConfirm = {
// Handle the actual deletion here
// For this example, we just close the dialog
showDeleteDialog = false
},
onDismiss = { showDeleteDialog = false }
)
}
}
@OptIn(ExperimentalMaterial3Api::class) // Required for ModalBottomSheet
@Composable
fun OptionsBottomSheet(
onDismiss: () -> Unit,
onOptionSelected: (String) -> Unit
) {
// Create a modal bottom sheet that slides up from the bottom
ModalBottomSheet(
onDismissRequest = onDismiss, // Called when user taps outside or swipes down
sheetState = rememberModalBottomSheetState() // Manages the sheet's state
) {
// Content inside the bottom sheet
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.padding(16.dp)
) {
// Header text for the bottom sheet
Text(
text = "Choose an Option",
style = MaterialTheme.typography.headlineSmall,
modifier = Modifier.padding(bottom = 16.dp)
)
// Create a button for each option
listOf("Edit", "Share", "Delete", "Report").forEach { option ->
TextButton(
onClick = {
// When an option is selected:
onOptionSelected(option) // Notify parent of selection
onDismiss() // Close the bottom sheet
},
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth() // Make button full width
) {
Text(option)
}
}
// Add some bottom spacing for better visual appearance
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(16.dp))
}
}
}
@Composable
fun DeleteConfirmationDialog(
onConfirm: () -> Unit,
onDismiss: () -> Unit
) {
// Create an alert dialog that appears in the center of the screen
AlertDialog(
onDismissRequest = onDismiss, // Called when user taps outside the dialog
title = { Text("Delete Item") }, // Dialog title
text = { Text("Are you sure you want to delete this item?") }, // Dialog message
confirmButton = {
// Button that confirms the action (destructive action)
TextButton(onClick = onConfirm) {
Text("Delete")
}
},
dismissButton = {
// Button that cancels the action (safe action)
TextButton(onClick = onDismiss) {
Text("Cancel")
}
}
)
}
Code Explanation
Let's break down each composable function to understand how bottom sheets and dialogs work together in this example.
MyScreen composable - The Coordinator
The MyScreen composable acts as the main coordinator that manages the state of both the bottom sheet and dialog. Here's how it works:
// State variables to control the visibility of overlays
var showDeleteDialog by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
var showOptionsSheet by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }These two state variables use remember and mutableStateOf to track whether each overlay should be visible. When set to true, the corresponding overlay appears.
// Button to show the options bottom sheet
Button(onClick = { showOptionsSheet = true }) {
Text("Show Options")
}
// Button to show the delete confirmation dialog directly
Button(onClick = { showDeleteDialog = true }) {
Text("Delete Item")
}The buttons trigger the overlays by setting the state variables to true. Notice how clicking "Show Options" opens the bottom sheet, and clicking "Delete Item" opens the dialog directly.
// Conditional rendering of the options bottom sheet
if (showOptionsSheet) {
OptionsBottomSheet(
onDismiss = { showOptionsSheet = false },
onOptionSelected = { option ->
when (option) {
"Delete" -> showDeleteDialog = true // Chain to dialog
"Edit" -> { /* Handle edit action */ }
"Share" -> { /* Handle share action */ }
}
}
)
}This demonstrates conditional rendering - the bottom sheet only appears when showOptionsSheet is true. The onDismiss callback closes the sheet by setting the state back to false. The onOptionSelected callback handles what happens when a user picks an option - notice how selecting "Delete" chains to show the dialog, creating a two-step confirmation flow.
// Conditional rendering of the delete confirmation dialog
if (showDeleteDialog) {
DeleteConfirmationDialog(
onConfirm = {
// Handle the actual deletion here
showDeleteDialog = false
},
onDismiss = { showDeleteDialog = false }
)
}Similarly, the dialog only renders when showDeleteDialog is true. Both onConfirm and onDismiss close the dialog, but onConfirm is where you would perform the actual deletion logic.
OptionsBottomsheet composable - The Bottom Sheet
The OptionsBottomSheet composable creates a modal bottom sheet that slides up from the bottom of the screen:
@OptIn(ExperimentalMaterial3Api::class) // Required for ModalBottomSheet
@Composable
fun OptionsBottomSheet(
onDismiss: () -> Unit,
onOptionSelected: (String) -> Unit
) {The @OptIn(ExperimentalMaterial3Api::class) annotation is required because ModalBottomSheet is still experimental in Material 3. The function takes two lambda parameters: one to handle dismissal and one to handle option selection.
ModalBottomSheet(
onDismissRequest = onDismiss, // Called when user taps outside or swipes down
sheetState = rememberModalBottomSheetState() // Manages the sheet's state
) {ModalBottomSheet is the Material 3 component that creates the bottom sheet. The onDismissRequest is called when the user wants to close it (by tapping outside or swiping down). The sheetState manages the sheet's animation and position state.
// Create a button for each option
listOf("Edit", "Share", "Delete", "Report").forEach { option ->
TextButton(
onClick = {
onOptionSelected(option) // Notify parent of selection
onDismiss() // Close the bottom sheet
},
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth() // Make button full width
) {
Text(option)
}
}This code creates a list of options dynamically. For each option, it creates a TextButton that fills the full width. When clicked, it notifies the parent composable about the selection and then closes the sheet. This pattern of notifying the parent and then dismissing is common - it allows the parent to handle the action while the sheet manages its own visibility.
DeleteConfirmationDialog composable - The Dialog
The DeleteConfirmationDialog composable creates a centered alert dialog for confirming destructive actions:
@Composable
fun DeleteConfirmationDialog(
onConfirm: () -> Unit,
onDismiss: () -> Unit
) {This composable takes two callbacks: one for when the user confirms the action and one for when they dismiss it. This separation is important because confirm and dismiss might have different behaviors.
AlertDialog(
onDismissRequest = onDismiss, // Called when user taps outside the dialog
title = { Text("Delete Item") }, // Dialog title
text = { Text("Are you sure you want to delete this item?") }, // Dialog message
confirmButton = {
TextButton(onClick = onConfirm) {
Text("Delete")
}
},
dismissButton = {
TextButton(onClick = onDismiss) {
Text("Cancel")
}
}
)AlertDialog is the Material 3 component for creating dialogs. Key features:
onDismissRequest: Called when the user taps outside the dialog or presses the back buttontitle: A composable that displays the dialog's titletext: A composable that displays the main messageconfirmButton: The button that confirms the action (typically the destructive action)dismissButton: The button that cancels the action (typically the safe action)
Notice that both buttons use TextButton, but in a real app, you might style the confirm button differently (e.g., with a red color) to indicate it's a destructive action.
Key Takeaways
- State Management: Use
rememberandmutableStateOfto control when overlays appear - Conditional Rendering: Use
ifstatements to show/hide overlays based on state - Callback Pattern: Pass lambda functions to child composables to handle user actions
- Chaining: You can chain overlays together (bottom sheet → dialog) for multi-step flows
- Dismissal: Always provide a way to dismiss overlays (swipe, tap outside, or cancel button)
How this example renders
Above is just a snippet of the code to view the full code, you need to go to my GitHub page and look at the chapter14 optionsDialog.kt file.
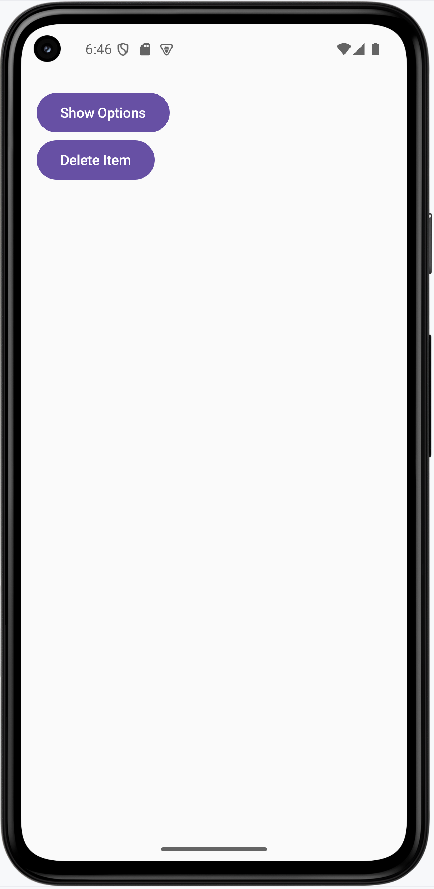
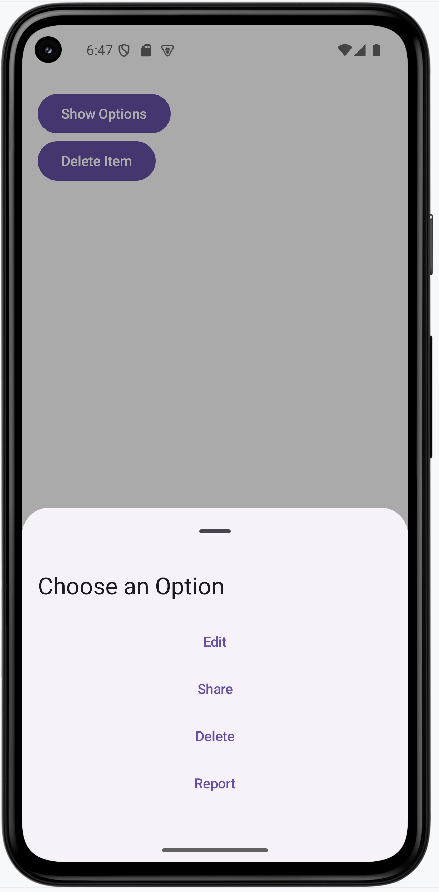
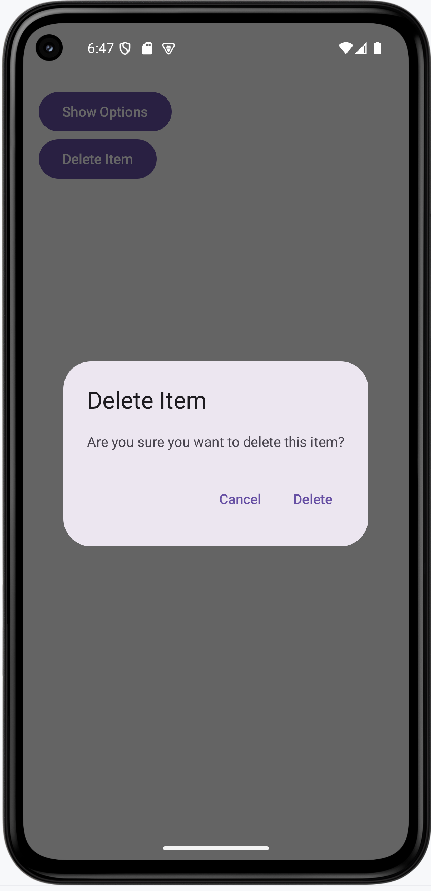
Tips for Success
- Use bottom sheets for multiple options and dialogs for single confirmations
- Always provide a way to dismiss bottom sheets and dialogs
- Keep dialog content focused and avoid overwhelming users
- Use appropriate titles and messages that clearly explain the purpose
- Test your bottom sheets and dialogs on different screen sizes
- Consider accessibility - make sure screen readers can navigate your dialogs
- Use consistent styling across all your dialogs and bottom sheets
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using dialogs for simple information that could be shown inline
- Creating bottom sheets that are too tall and hard to dismiss
- Not providing clear action buttons in dialogs
- Forgetting to handle the dismiss action properly
- Using too many nested dialogs or bottom sheets
- Not considering the user's context when showing dialogs
- Making dialogs or bottom sheets too complex with too many options
Best Practices
- Use bottom sheets for actions that don't require immediate attention
- Use dialogs for critical decisions or important information
- Keep dialog content concise and focused on a single task
- Provide clear, descriptive button labels
- Use consistent visual design across all your overlays
- Consider the user's workflow when deciding between bottom sheets and dialogs
- Test your overlays with different content lengths and screen sizes
- Use appropriate animations and transitions for a polished feel