Drawers and Tabs
Drawers and Tabs?
Think of navigation drawers and tabs like the organization system in a library. Navigation drawers are like the main catalog that slides out from the side, showing you all the different sections (like fiction, non-fiction, science, etc.). Tabs are like the dividers in a filing cabinet - they help you quickly switch between related categories without losing your place.
Navigation drawers slide in from the left side of the screen and contain your app's main navigation menu. Tabs appear at the top of the screen and let users switch between different views or sections of your app. Both help users navigate your app efficiently and find what they're looking for.
Quick Reference
| Component | Description | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| Navigation Drawer | Slides in from left side with main menu | Main app navigation, settings, user profile |
| Top Tabs | Horizontal tabs at top of screen | Switching between related content sections |
| Tab Row | Scrollable row of tabs | Many categories that don't fit on screen |
When to Use Navigation Drawers and Tabs
Use Navigation Drawers When:
- You have many main sections in your app (5+ items)
- You want to save screen space for content
- You need to access settings, profile, or help sections
- You want to provide quick access to all app features
- You're building a complex app with multiple main areas
Use Tabs When:
- You have 2-5 related content sections
- Users need to switch between different views frequently
- You want to show related content side by side
- You're organizing content by categories or types
- You want to keep navigation visible and accessible
Common Components and Options
| Component | What It Does | When to Use It |
|---|---|---|
| DrawerState | Manages the open/closed state of the drawer | When you need to control drawer programmatically |
| TabRow | Creates a horizontal row of tabs | For top-level navigation between sections |
| Tab | Individual tab in a tab row | For each section or category in your app |
| TabPosition | Defines the position and styling of tabs | When you need custom tab appearance |
Practical Examples
Basic Navigation Drawer
@Composable
fun MyAppWithDrawer() {
val drawerState = rememberDrawerState(initialValue = DrawerValue.Closed)
val scope = rememberCoroutineScope()
ModalNavigationDrawer(
drawerState = drawerState,
drawerContent = {
ModalDrawerSheet {
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(12.dp))
Text(
"My App",
modifier = Modifier.padding(16.dp),
style = MaterialTheme.typography.titleMedium
)
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(12.dp))
NavigationDrawerItem(
icon = { Icon(Icons.Default.Home, contentDescription = null) },
label = { Text("Home") },
selected = false,
onClick = { /* Navigate to home */ }
)
NavigationDrawerItem(
icon = { Icon(Icons.Default.Person, contentDescription = null) },
label = { Text("Profile") },
selected = false,
onClick = { /* Navigate to profile */ }
)
NavigationDrawerItem(
icon = { Icon(Icons.Default.Settings, contentDescription = null) },
label = { Text("Settings") },
selected = false,
onClick = { /* Navigate to settings */ }
)
}
}
) {
// Your main app content here
Column {
TopAppBar(
title = { Text("My App") },
navigationIcon = {
IconButton(onClick = { scope.launch { drawerState.open() } }) {
Icon(Icons.Default.Menu, contentDescription = "Menu")
}
}
)
// Rest of your content
}
}
}This creates a navigation drawer that slides in from the left when the menu button is tapped. The drawer contains navigation items for Home, Profile, and Settings, each with an icon and label.
Top Tabs with Content
@Composable
fun TabbedContent() {
var selectedTabIndex by remember { mutableStateOf(0) }
val tabs = listOf("Recent", "Popular", "Favorites")
Column {
TabRow(selectedTabIndex = selectedTabIndex) {
tabs.forEachIndexed { index, title ->
Tab(
selected = selectedTabIndex == index,
onClick = { selectedTabIndex = index },
text = { Text(title) }
)
}
}
when (selectedTabIndex) {
0 -> RecentContent()
1 -> PopularContent()
2 -> FavoritesContent()
}
}
}
@Composable
fun RecentContent() {
LazyColumn {
items(10) { index ->
ListItem(
headlineContent = { Text("Recent Item ${index + 1}") },
supportingContent = { Text("This is a recent item") }
)
}
}
}This creates a tabbed interface with three tabs at the top. Users can tap on any tab to switch between different content sections. The content changes based on which tab is selected.
Scrollable Tab Row
@Composable
fun ScrollableTabs() {
var selectedTabIndex by remember { mutableStateOf(0) }
val categories = listOf(
"All", "Technology", "Science", "Sports", "Entertainment",
"Politics", "Business", "Health", "Education", "Travel"
)
Column {
ScrollableTabRow(
selectedTabIndex = selectedTabIndex,
edgePadding = 16.dp
) {
categories.forEachIndexed { index, category ->
Tab(
selected = selectedTabIndex == index,
onClick = { selectedTabIndex = index },
text = { Text(category) }
)
}
}
// Content based on selected tab
when (selectedTabIndex) {
0 -> AllContent()
1 -> TechnologyContent()
// ... other content
}
}
}This creates a horizontally scrollable tab row that's perfect when you have many categories. Users can scroll through the tabs and tap to select one. The edgePadding ensures the first and last tabs aren't cut off.
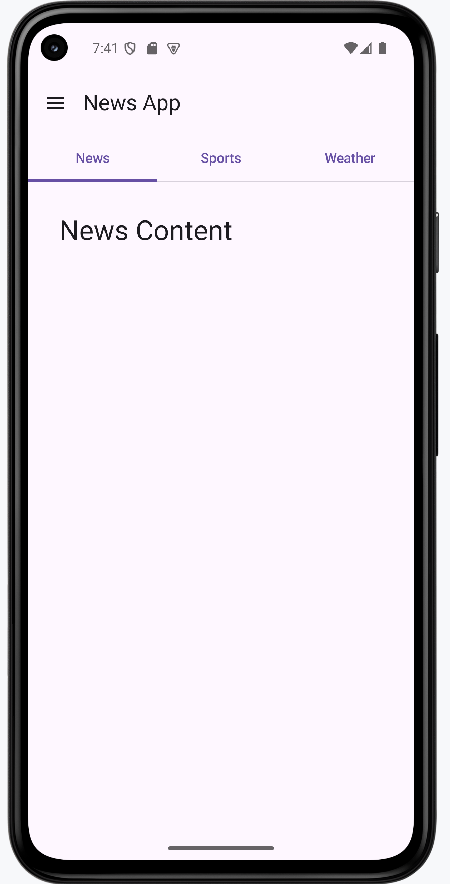
Combining Drawer and Tabs
@Composable
fun AppWithDrawerAndTabs() {
val drawerState = rememberDrawerState(initialValue = DrawerValue.Closed)
val scope = rememberCoroutineScope()
var selectedTab by remember { mutableStateOf(0) }
val tabs = listOf("News", "Sports", "Weather")
ModalNavigationDrawer(
drawerState = drawerState,
drawerContent = {
ModalDrawerSheet {
Text("News App", modifier = Modifier.padding(16.dp))
NavigationDrawerItem(
icon = { Icon(Icons.Default.Home, null) },
label = { Text("Home") },
selected = false,
onClick = { /* Navigate */ }
)
NavigationDrawerItem(
icon = { Icon(Icons.Default.Settings, null) },
label = { Text("Settings") },
selected = false,
onClick = { /* Navigate */ }
)
}
}
) {
Scaffold(
topBar = {
TopAppBar(
title = { Text("News App") },
navigationIcon = {
IconButton(onClick = { scope.launch { drawerState.open() } }) {
Icon(Icons.Default.Menu, "Menu")
}
}
)
}
) { padding ->
Column(modifier = Modifier.padding(padding)) {
TabRow(selectedTabIndex = selectedTab) {
tabs.forEachIndexed { index, title ->
Tab(
selected = selectedTab == index,
onClick = { selectedTab = index },
text = { Text(title) }
)
}
}
when (selectedTab) {
0 -> NewsContent()
1 -> SportsContent()
2 -> WeatherContent()
}
}
}
}
}This combines both a navigation drawer and tabs. The drawer provides access to main app sections, while the tabs let users switch between related content within the current section.
How this example renders
Above is just a snippet of the code to view the full code, you need to go to my GitHub page and look at the chapter14 drawerTab.kt file.

Learning Aids
Tips for Success
- Use navigation drawers for apps with many main sections (5+)
- Use tabs for 2-5 related content sections
- Keep tab labels short and descriptive
- Use appropriate icons for navigation items
- Consider the user's mental model when organizing navigation
- Test navigation on different screen sizes
- Provide visual feedback for selected states
- Use consistent navigation patterns throughout your app
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using too many tabs (more than 5 can be overwhelming)
- Putting unrelated items in the same navigation drawer
- Not providing clear visual feedback for selected items
- Using navigation drawers for simple apps with few sections
- Making tab labels too long or unclear
- Not considering how navigation works on different screen sizes
- Forgetting to handle navigation state properly
- Using inconsistent navigation patterns
Best Practices
- Choose navigation based on the number and relationship of your content sections
- Use descriptive labels and appropriate icons for navigation items
- Provide clear visual feedback for the current selection
- Keep navigation consistent across your entire app
- Consider the user's workflow when organizing navigation
- Test navigation on different devices and screen orientations
- Use Material Design guidelines for navigation patterns
- Provide alternative navigation methods for accessibility