CPS251
Android Development
Animations and Transitions in Material Design
Introduction
Animations and transitions are like the body language of your app—they help users understand what's happening, guide their attention, and make your app feel alive. In Material Design, motion isn't just for decoration; it helps users follow changes and makes your app more enjoyable to use. Jetpack Compose gives you easy tools to add smooth, meaningful animations to your UI, even if you've never done it before.
When to Use Animations and Transitions
- To show changes in state (for example, expanding a card or switching tabs)
- To guide the user's attention to important actions or new content
- To make your app feel more polished and professional
- To provide feedback (like a button press, loading spinner, or error message)
Common Animation Tools in Compose
| Tool | What It Does | When to Use It |
|---|---|---|
animate*AsState | Animates a value (like color, size, or position) smoothly from one state to another | For simple state changes, like making a button grow when pressed |
AnimatedVisibility | Animates showing or hiding content (fades, slides, etc.) | For expanding/collapsing UI, like showing extra details |
updateTransition | Coordinates multiple animations at once | For more complex transitions, like animating several properties together |
rememberInfiniteTransition | Creates looping or repeating animations | For effects like pulsing, spinning, or loading indicators |
Crossfade | Animates switching between two composables with a fade effect | For smoothly changing screens or content |
Animatable | Gives you manual control to animate to specific values, interrupt, or chain animations | For custom or interactive animations |
AnimationSpec | Customizes the timing, speed, and feel of your animations (spring, tween, keyframes, etc.) | When you want to fine-tune how your animation moves |
Transition | Animates multiple values together with more control | For advanced, coordinated animations |
Practical Example: Animated Card with Multiple Effects
@Composable
fun AnimatedCardExample() {
// State variables for animations
var expanded by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
var showDetails by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
// Animated values
val cardColor by animateColorAsState(
targetValue = if (expanded) Color(0xFFBBDEFB) else Color.White,
label = "cardColor"
)
val cardElevation by animateDpAsState(
targetValue = if (expanded) 26.dp else 4.dp,
label = "cardElevation"
)
val cardWidth by animateDpAsState(
targetValue = if (expanded) 300.dp else 200.dp,
label = "cardWidth"
)
// Card with animated properties
Card(
colors = CardDefaults.cardColors(
containerColor = cardColor
),
elevation = CardDefaults.cardElevation(
defaultElevation = cardElevation
),
modifier = Modifier
.width(cardWidth)
.padding(16.dp)
.padding(top=50.dp)
.clickable {
expanded = !expanded
showDetails = expanded
}
) {
Column(modifier = Modifier.padding(16.dp)) {
Text(
text = "Tap to ${if (expanded) "collapse" else "expand"}",
style = MaterialTheme.typography.titleLarge
)
// Animated visibility for additional content
AnimatedVisibility(visible = expanded) {
Column {
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(8.dp))
// Crossfade animation between states
Crossfade(targetState = showDetails) { detailsVisible ->
if (detailsVisible) {
Text("Here are more details! This text fades in.")
} else {
Text("Tap to see more details.")
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
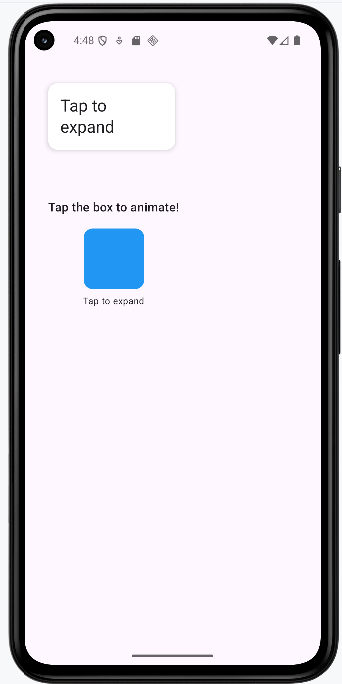
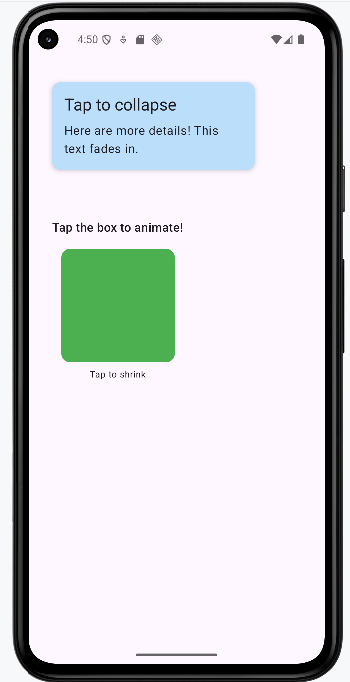
@Composable
fun AnimatedBoxExample() {
// State variable to track if box is expanded
var isExpanded by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
// Animated size using animationSpec with tween()
// tween() allows us to specify duration in milliseconds
val boxSize by animateDpAsState(
targetValue = if (isExpanded) 150.dp else 80.dp,
animationSpec = tween(
durationMillis = 500, // Animation duration: 500ms
// easing = FastOutSlowInEasing (default) - starts fast, ends slow
),
label = "boxSize"
)
// Animated color for visual feedback
val boxColor by animateColorAsState(
targetValue = if (isExpanded) Color(0xFF4CAF50) else Color(0xFF2196F3),
animationSpec = tween(durationMillis = 500),
label = "boxColor"
)
Column(
modifier = Modifier.padding(16.dp),
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally
) {
Text(
text = "Tap the box to animate!",
style = MaterialTheme.typography.titleMedium,
modifier = Modifier.padding(bottom = 16.dp)
)
// Animated box
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.size(boxSize)
.background(
color = boxColor,
shape = RoundedCornerShape(12.dp)
)
.clickable {
isExpanded = !isExpanded
}
)
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(8.dp))
Text(
text = if (isExpanded) "Tap to shrink" else "Tap to expand",
style = MaterialTheme.typography.bodySmall
)
}
}
- What does this example do? This card animates its color, elevation (shadow), and width when you tap it. When expanded, it also reveals extra details with a fade-in effect using
CrossfadeandAnimatedVisibility. - How does it work?
animateColorAsState,animateDpAsState, andAnimatedVisibilitywork together to animate the card's appearance and content.Crossfadesmoothly switches between two pieces of text. - Why use this? Combining multiple animation tools makes your UI feel more dynamic and helps users understand what's changing. This example shows how you can animate several properties and content at once, all with simple Compose code.
How this example renders
Above is just a snippet of the code to view the full code, you need to go to my GitHub page and look at the chapter13 animation.kt file. When you run the code it will look like the example below.
Tips for Success
- Use animations to clarify what's happening, not just to decorate
- Keep animations quick and smooth—most should finish in under 300ms
- Test on real devices to make sure animations look good and don't slow things down
- If you're not sure, start simple! Even a small animation can make a big difference
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Overusing animations so your app feels slow or distracting
- Using animations that don't match Material Design guidelines (like odd timing or movement)
- Making animations too long or too flashy—users want to get things done!
- Forgetting to test on different devices (animations can look different on slow phones)
Best Practices
- Use motion to guide and inform, not just to decorate
- Follow Material Design's motion guidelines (see Google's docs for details)
- Keep your animations consistent across the app—use the same timing and style everywhere
- Comment your code to explain why you're animating something, especially if it's not obvious